Archive Post
Google and Levi’s partner together to create ‘Smart Jacket’
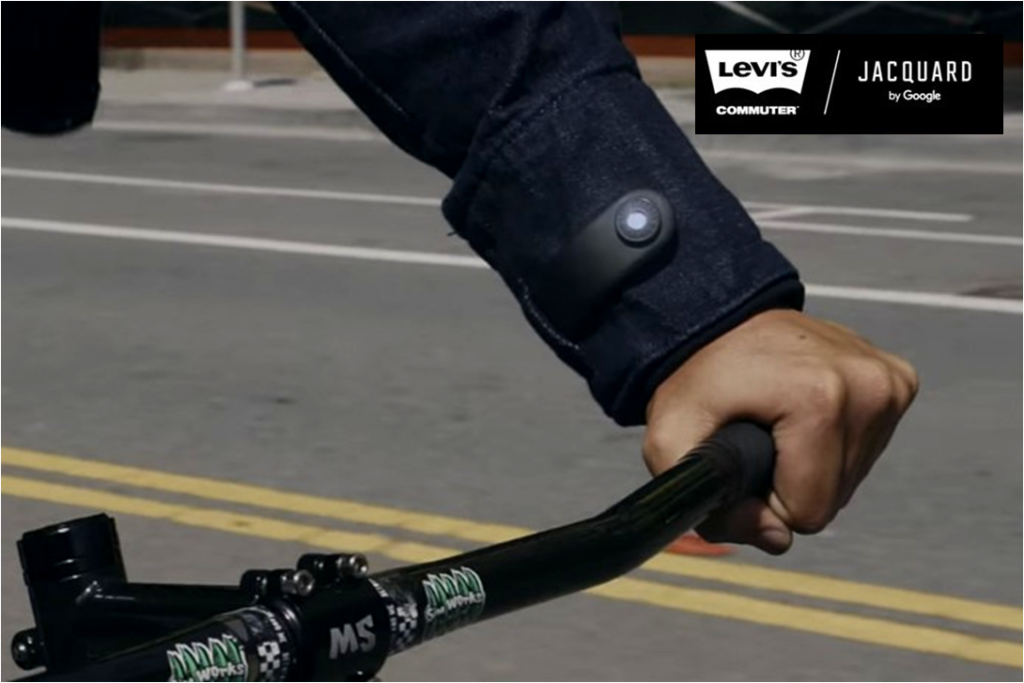
Smart jacket in town? Google and Levi’s Denim have entered into a partnership to develop a smart jacket using a technology codenamed Project Jacquard that lets users interact with their Smartphones by swiping at the garment in various ways. Jacket, also known as ‘Computer Trucker Jacket’ is designed mainly for cyclists who can control their phones safely while riding.
Google’s Advanced Technology and Projects (ATAP) division partnered with Levi to utilize its Project Jacquard technology, announced last year, centered around connected textiles and clothing. The tech, which is basically composed of conductive fabric woven into the garment to create an interactive patch that senses touch, pressure and even your hand’s position before you touch the fabric. Jacket contain a weave of the Jacquard interactive threading on the left arm and a Bluetooth-enabled loop to connect to the cuff of the jacket. That cuff lets your phone talk to the jacket, and you can configure exactly what gesture you want to work with which apps. For example, you can adjust the volume on your music, tap to change the track or even use gestures to get navigation directions from Google maps. Currently Jacquard is restricted to only calls, messaging apps, Google Play music, Maps and third party apps from Spotify and Strava. The Project Jacquard garment will be available in spring 2017 and not much is known about the cost of the garment.
The Jacket is manufactured pertaining to the Levi’s standard manufacturing techniques and doesn’t need any special care. Only the Bluetooth cuff needs to be removed before washing it. Google wants to develop more apps and technology and enter athletic clothing as it would be more appealing and cater large audience.
Latest announcements from Google’s I/O 2016 will surely blow your mind
Google announced welcoming news on its latest I/O. To start with VR(Virtual Reality) , there have been 50 Million downloads of its virtual reality apps for the Cardboard platform from the Play Store. This is an important step for virtual reality on mobile, and more importantly, it shows developers that there is demand for this sort of thing. In its latest conference it has announced that it will delve deeper into the realm of virtual reality with a system called Daydream which will be available to users end of the year. Google will sell this virtual-reality headset with a wireless motion controller with the Nexus brand that the company original created as a showcase for its Android operating system for smartphones.
Google wants to change how people manage their daily lives. So it will introduce a personable form of artificial intelligence into an Internet-connected device called Home. Google touted its Home speaker as a more intelligent and versatile device, mostly because it can tap into the same stockpile of information that makes Google’s Internet search place so popular. Google also has redesigned its virtual assistant to be more conversational and intuitive. It will be the voice and brains inside Google Home. Home even integrates with third-party services, allowing you to do things like call an Uber car or book a restaurant reservation using OpenTable.
One of the biggest announcements that Google made was a feature called Instant Apps. It will have the ability to run on device without even installing them. Instant Apps is Google’s answer to the pain of installing phone apps you know you’ll use just once or twice, for shopping or booking a parking spot, for example. With this approach, the app runs on Google’s servers instead of your phone. Only the parts you need are sent to your phone on an as-needed basis.
Google search changed the world, literally. Now, Google Assistant is the natural extension of search, supporting “conversational understanding” to make search more natural and to better support voice searches. It has also announced a chat service called Allo. It will draw a vast database to predict how a user might want to respond to a text and automatically fetch links to video clips and other relevant information to an ongoing conversation. Duo will be Google’s companion app for Allo that adds in video calling. For example, Knock Knock lets users see the incoming video call feed before even answering the call. This way, the receiving party can see whose calling and where they are before they even pick up the call.
Google’s next major mobile software release is Android N, and it’s going to be a huge update when it’s released later this year. Performance and graphics improvements are a big part of Android N. Most impressively perhaps, Android N will download and install system updates automatically. Moving on to the app switcher screen, Android will automatically remove apps from the UI when it determines the app is no longer needed. This way, the app switcher UI is decluttered and it’s easier to find the app you’re looking for. There’s also a new quick switch function accessed by double-tapping the recent button on a phone or tablet. Although the upcoming products will offer some unique features, they mostly painted a picture of a company scrambling to catch up with its rivals.
Penalty on Telecom companies relaxed as court rules out TRAI’s directive for call drop
What are these issues regarding call drop? Supreme Court struck down the TRAI’s (Telecom Regulatory Authority of India) directive imposing for call drops on telecom operators. Major issue is that a lot of subscribers belong to low income group (wage earners) who recharge for Rs 10 to Rs 20 coupons. A call drop is a pinch in their pockets and eventually they are left with no option but to make another call. This again adds to their misery. To combat such a situation telecom regulator TRAI had proposed to penalize telecom companies at Rs 1 per call drop up to a maximum of three calls a day, to be credited to the calling customers account. It is this infirmity that led to strike down the order as ambiguous.
The Court pointed out that call drops cannot exceed two percent of the calls. The majority of service providers claimed it to be under two percent. TRAI has failed to look into other factors behind the call drop such as paucity of spectrum, radio interference from neighbouring cells, shortage of mobile towers, and problems of clearance from agencies. Faulty handsets and manipulation by consumers add to the call drop issue as well.
The call drop problem is real. Consumers are charged for the full time even when the call breaks in the first few seconds. Operators make gains from this. The court has said that Parliament can enact a call drop compensation rule without detracting from the regulatory powers of the TRAI. TRAI needs to grant more spectrum and mobile phone towers to the telecom companies. A lot of issues might arise, such as resistance from locals to installing of tower and clearance from local authorities. These needs consideration and good consultation. It is time that telecom companies take responsibility for any deficiency of service because the consumer wants a solution and not compensation.
‘112’ will be India’s all-in-one emergency number from January 1, 2017.
Indians will now be a call away from any kind of distress situation. The single number provision would be similar to the ‘911’ all-in-one emergency service in the US. Users having SIMs and landline whose outgoing facility are abandoned or temporary suspended, can also avail the service by dialing 112. Calls will be diverted to the concerned department without any extra waiting time. User will make communication through SMSs, or call and the system will learn about the location of the caller. This will then be shared with the nearest help centre. People will be able to feed ‘112’ in panic button system which will also be available on all mobile phones from January 1 under the law. It will enable users to make emergency call or send alerts to multiple numbers just by pressing a button.
Currently India has different communication and response system such as police (100), fire brigade (101), ambulance (102) and Emergency Disaster Management (108). All existing emergency numbers will be phased out within a year of rolling out 112, depending upon the awareness about this new facility. An inbuilt GPS navigation system would be mandatory for all phones a year later with effect from January 1, 2018. The emergency service calls will also be supported through a call centre like facility, which will have representatives speaking in Hindi, English and the local language. The existing call centres which handle emergency number calls will be asked to handle calls on 112 as well. And additional capacity is being worked out by the department.
NDA Government on a mission to deploy mobile connectivity to more than 55000 villages by 2019
Increasing demand for mobile has led the NDA government to deploy it to small towns and villages across the country. The Government plans to phase out broadband connection in more than 55,669 villages by March 2019. The move, by the department of telecommunication, includes the project to connect over 8,600 villages in the north-eastern region of the country. Villages will be connected by installing 321 mobile tower sites by September 2017. The Project has been approved at an estimated cost of Rs 5336.18 crore.
Telecom has confirmed installing of the optic fibres in 48199 gram Panchayats. For deeper digital penetration in rural areas, the government has taken up the BharatNet project in mission mode to connect all 2.50 lakh gram Panchayats, which have over 600 million people. It will support e-governance services, e-commerce, tele-medicine, tele-education, financial services, among others. Connectivity in areas affected by left wing extremism (LWE), a total of 1517 towers out of 2199 identified by Ministry of Home Affairs have started functioning till date. Penetration in rural areas will open windows to mobile operators and cable TV operators to launch next generation services and create employment opportunities for the locals.
Technology turns Arm into a Touchpad to control Smartwatch
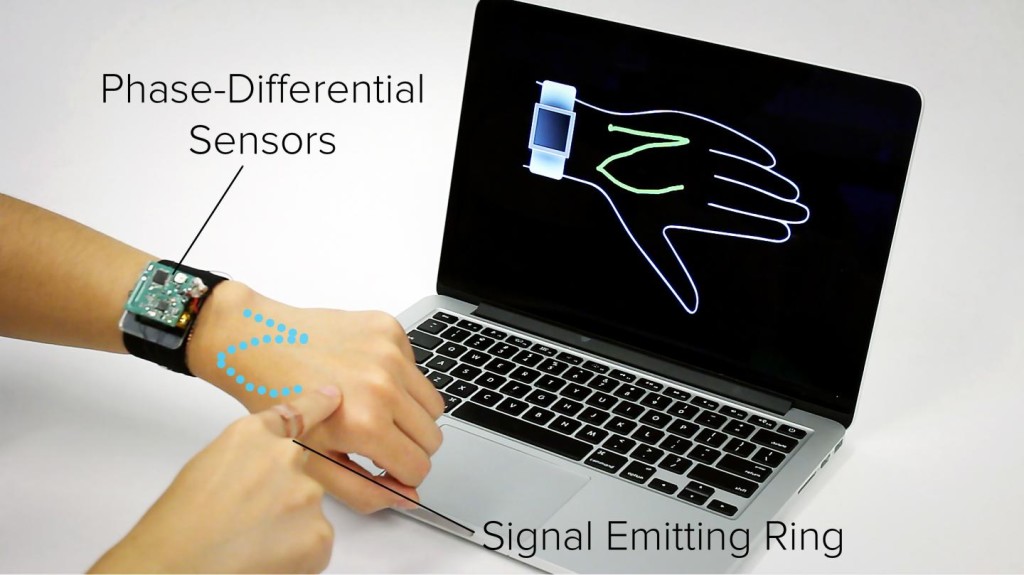
A new technology developed at Carnegie Mellon University by the Human-Computer Interaction Institute’s Future Interfaces Group, enables users to turn their entire lower arm into a touchpad for controlling Smartwatches. This technology, called the SkinTrack allows continuous tracking on the hands and arms. It can detect touches at discrete locations on the skin, enabling functionality similar to buttons. The user wears only a signal- emitting ring which propagates an electromagnetic wave in the skin that can be localized with sensors worn on the wrist.
The biggest advantage of SkinTrack is that it is not obstructive. It provides a larger interface for the users compared to the Smartwatches and digital jewellery where the interaction area is small because most of the area is covered with finger. By using electrodes integrated into the watch’s strap, it’s possible to pinpoint the source of those electromagnetic waves because the phase of the waves will vary. Electrodes corresponding to the 12 o’clock and 6 o’clock positions on the watch, for instance, can detect phase differences that can determine the position of the finger along the width of the arm; electrodes at the 3 o’clock and 9 o’clock positions can determine the finger’s position along the length of the arm.
SkinTrack technology has various other functions such as a game controller, to scroll through lists on the Smartwatch, to zoom in and out of onscreen maps and to draw. A number pad application enabled users to use the back of the hand as a dial pad, hovering a finger over the hand as a cursor, highlighting numbers on the screen to aid in targeting touch points.
So far this wearable technology is safe. The radio frequency signal does not have an impact on the health of the user. Human body is accustomed to using daily appliances right from current drawn from the finger by touch screen to the electromagnetic noise from florescent lights with no ill effects.
India gets its own GPS with IRNSS-1G Satellite launch
India is not far behind the developed nations. The country is on a mission to get its own version of Global Positioning System (GPS). An Indian Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) rocket lifted off successfully with the country’s seventh satellite, IRNSS-1G (India Navigation Satellite System) from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota near Chennai on April 29. It consists of a constellation of seven satellites of which six – IRNSS-1A, IRNSS-1B, IRNSS-1C, IRNSS-1D, IRNSS-1E and IRNSS-1F- have already been put into orbit. It is like a position information portal of the entire country and covers around 1500km around the Indian mainland (boundaries). It stands tall at 44.4 meters and weighs around 320 tonnes. The rocket would put IRNSS-1G into orbit at an altitude 497.8 km. It has a life span of 12 years.
ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) has set up a ground facility across 18 different locations which will be responsible for satellite ranging and monitoring, generation and transmission of navigation parameters, etc. Users will have a position accuracy of better than 20 meters. The IRNSS will offer two types of services namely Standard Positioning Services for all users and Restricted Services (RS) which will be provided only to the authorized users. The restricted service will be used by the military for missile delivery and navigation and tracking of aircraft. Other applications of IRNSS include aerial and marine navigation, disaster management, vehicle tracking and fleet management, Search and Rescue (SAR) operations, Mining and Surveying and other Mapping operations. With the constellation of satellites complete, India has joined the league of countries that has an indigenous navigation system. Thus marks the beginning of a developed nation, reducing dependency on the US Global Positioning System.
‘Panic Button’ will now ensure a safe nation for women!
Women will now have an option to signal a family member or police authorities in distress situation by pressing a panic button in their respective mobile handsets. The Ministry of Women and Child Development had taken up the issue of installation of a physical panic button on mobile phones as one of the initiatives in June 2014.The Department of Telecommunications has notified the “Panic Button and Global positioning Systems in Mobile Phones Handsets Rules 2016″. Under these rules, effective from January 2017, all feature phones will have the facility of panic button configured to the numeric key 5 or 9 and all smart phones will have the panic button configured to three times short pressing of the on-off button. Further, from January 2018 all mobile phones will be required to have the facility of identifying the location through satellite based GPS.
The minister of Women and Child Development will now be working with DOT and other stakeholders to ensure that similar solutions be made available for existing handsets in the form of software patches. These software patches will be available for direct download in Smartphones and an installation at the mobile phone shops by concerned manufacturers/service provider. Reports of attacks on women in India have reverberated around the world, increasing pressure on officials to make the country a safer place. Technology will make human life better and what better than using it for the security of women.
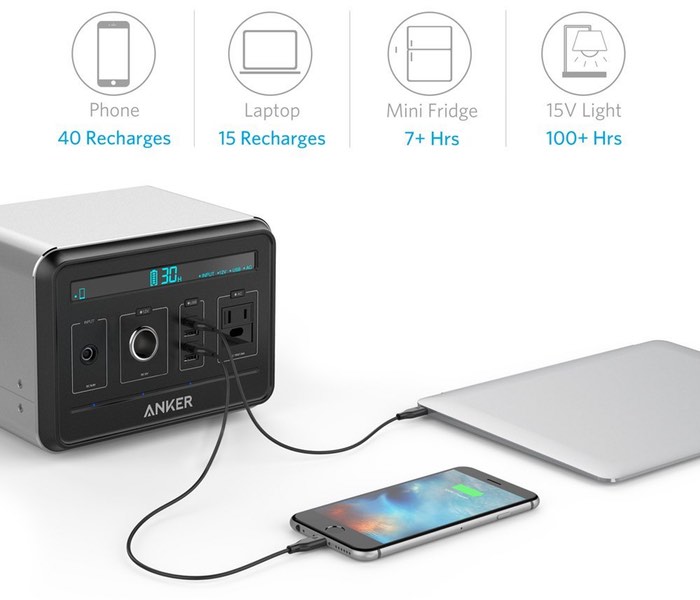
Portable battery charger by Anker can charge your phone up to 40 days!
How much power does your Smartphone support through the day?On an average it provides around 2500 mAh (Milliampere hour) of power. Anker may have a solution for this scenario. The company best known for its pocket-sized lithium-polymer batteries has released 120,600 mAh power supply aptly named the Powerhouse. The company launched the machine on April 18, and it definitely has more uses than a mere phone charger with its multi-charging ability.
The Powerhouse has a host of connections which includes 12V (Volt) car charger slot, four 2.4A USB ports, a 16.8V power input space and an 110V standard AC plug. The power bank can be recharged in 10 hours using the kit charger and in 16 hours in future with a solar charger that is yet to be released. The LCD panel at the helm displays which ports are switched on, along with an accurate prediction of how much time remains for the machine to tap out. It also includes temperature and voltage safety controls as well as an internal surge protection that prevents the machine from turning into a heat-induced bomb.
It measures 7.9″ x 6.5″ x 5.7″, and it weighs in at 9.3lbs. It will probably come in handy if you are in the areas where running electricity isn’t reliable or readily available. The Powerhouse is said to be able to charge a Smartphone 40 times before being depleted. Alternatively it can also charge laptops, mini fridges, or even power a 15V light bulb for more than 100 hours. Currently it is selling the device through Amazon.
SIM cards to revolutionize Machine to Machine Communication
Ever Heard of SIMs for Machine? The answer would be no. Yet it is going to be a possible innovation in a few days. Machine-to-Machine communication (M2M) in devices like CCTV cameras and ACs will be possible and deployed mainly in the smart cities. Department of Telecom will issue ‘Know your customer’ guidelines to ensure availability of mobile SIM cards for such equipments. A provision for SIM transfer would be initiated because devices will change hands. There would be no tele-verification whatsoever. Some communication would be allowed on platforms such as SMSs, Voice and Data but on a pre-defined number. For such M2M services, SIM card will be issued in bulk. Certain norms and regulations will be applicable on these SIMs and mostly these regulations will facilitate development of smart cities which have devices with sensors that will communicate using SIMs or internet connection.
Apart from M2M communication, government body will look at encryption, privacy and security from an Indian perspective. Department of Telecom will soon have a virtual network operator license – the third license, which seeks to separate network operations from delivery of services. Such a VNO (Virtual Network Operator) license would help system Integrator to get into agreement with telecom operators for providing M2M services. The M2M segment is expected to revolutionize the telecom sector at a more rapid pace compared to the sale of SIM for mobile communication.