Telemedicine – A life Saver!
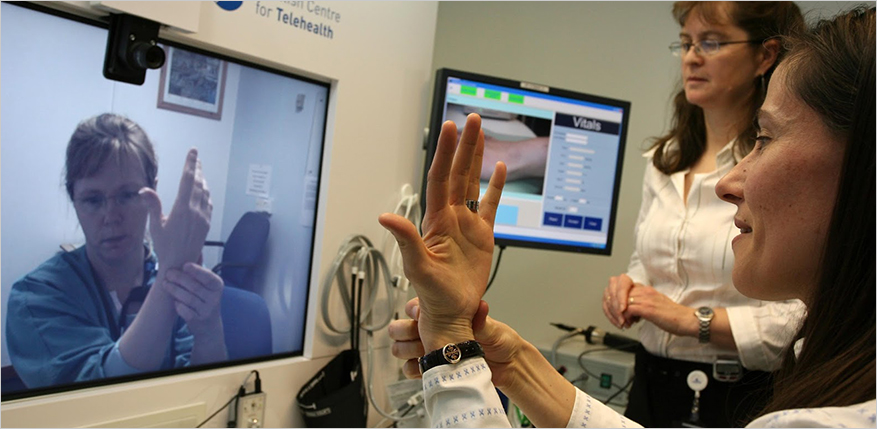
What is Telemedicine? Telemedicine uses video conferencing and other telecommunication tools to deliver healthcare at a distance. It promises patients greater convenience and time saved. For medical clinics and hospitals, it delivers time, money, and resource savings. In rural areas with fewer medical facilities, telemedicine promises better healthcare for residents.
Telemedicine provides access to healthcare information and records, enables access to specialists, improves communication between doctors and patients, and helps professionals gather and share important health data.
Technology supports telemedicine
A number of technologies make telemedicine a practical reality. Video conferencing plays a key role, together with secure, low-cost mobile communications that support real-time collaboration through tablets and smartphones.
Video conferencing is available on mobile devices with a high-speed Internet connection and softphone, a software application. Because video conferencing reach any location with Internet access, a mobile collaboration between doctors and colleagues or doctors and patients can occur inside hospitals, medical centers, and anywhere in the country, even remote rural areas.
Healthcare professionals transmit data such as electronic records and other documentation securely. In addition to real-time video collaboration, doctors use recorded video content to support patient education, aftercare, and wellness programs in the community
Improving collaboration within hospitals
In hospitals, doctors and nurses frequently move between wards, visiting patients. To seek advice or collaborate with specialists, they connect and share patient information via the hospital’s internal wireless networks using smartphones or tablets.
Increasing access to specialists
To see and assess a patient over live video within minutes of arrival at the hospital. The faster a patient receives stroke treatment, the better chances they will recover without permanent disability. Video collaboration is accelerating ‘door to needle’ treatment by minutes, sometimes even hours, time-saving that could change a person’s life forever.
Changing the pattern of patient visits
As an alternative to a home visit, doctors may video or Web conference with patients with less mobile or medically unable to visit a health center. Doctors discuss the patient’s condition and recommend medication or treatment.
Remote monitoring systems grant access to critical patient data, like those with heart conditions or diabetes. This reduces home visits for routine assessments and provides timely alerts of changes in patients’ conditions that may require urgent attention.
Reducing hospital readmissions
Many hospitals find that readmissions put further pressure on their already limited resources. Although patients receive aftercare instructions before being discharged, when problems occur, patients are readmitted for further treatment or support. There are five areas that frequently lead to hospital readmissions:
- Hospitals creation and implementation of effective discharge plans.
- Patient non-compliance with medication and care instructions.
- Compromised follow-up care due to poor collaboration.
- Family caregivers not connected or informed to assist with care.
- Patient condition deteriorates and necessary care not accessed.
Video collaboration and content management solutions help hospitals to deal with these challenges.
To improve patient discharge plans, hospitals can offer live, collaborative video at the time of discharge. A live conversation ensures patients, caregivers, and family members participate in the creation of a discharge plan and fully understand what action to take as the patient returns home.
Hospitals may also create a video recording explaining the discharge plan for the patient and family. The information explains what to expect in a normal recovery, compared to symptoms that represent a risk to the patient.
If patients forget the care instructions or have difficulty with their medication, the hospital sends reminders via real-time video collaboration or a pre-recorded video library. This makes reviewing patient care easy.
As part of the recovery process, patients and caregivers benefit from the support of their assigned healthcare providers. They can have virtual access to their primary care physician, case manager, or other professionals via live video. These video follow-ups help long-term patients benefit from feeling connected to their continued care.
Video collaboration assists the patients’ family who may live outside the area but want to participate in the care process. Family members can participate in video calls to create home care plans, learn to recognize risks, and assist with communication.
If a long-term patient’s condition changes or deteriorates, video collaboration enables access to their care team without resorting to readmission. Real-time video interaction helps case managers, nutritionists, physical therapists, primary care physicians, and others adapt treatment plans as changes occur in health and behavior.
Improving access to rural healthcare
In remote areas with limited medical resources, telemedicine provides local doctors a higher standard of care for their patients. Besides the opportunity for virtual home visits, telemedicine gives local professionals access to specialists anywhere in the country.
Local doctors gain insight into cases and procedures beyond their own experience or skills. It assists the diagnosis of complex cases, even allowing surgeons to conduct complex procedures with live video under the direction of a remote expert.
Supporting preventative care in the community
Telemedicine is playing an important role in preventative medicine. As part of the National Prevention Strategy, video conferencing enables hospitals, clinics, health departments, community health centers, community colleges, and facilities like rehab centers and skilled nursing facilities to collaborate and provide community-based services that contribute to the health and wellness of the public.
In smoking cessation programs or alcohol and drug abuse prevention, community teams utilize pre-recorded educational content or hold live interactive video sessions. They hear from experts in the field and discuss issues with doctors and nurses as well as peers in the community who struggle with similar problems.
Changing attitudes
Despite the promise and recent accomplishments of telemedicine, barriers to its wider adoption remain. A study by The Economist Intelligence Unit found 49 percent of respondents believe patients would be concerned about the risk of data breaches.
Although video collaboration is capable of providing benefits throughout the healthcare industry, professionals must be aware of privacy issues. Any organization providing doctors, nurses, and other workers with remote access to patient data must ensure the security of data transmitted by video or other communication channels.
Some insurers refuse to support telemedicine due to increased costs for fewer perceived health benefits. And, State medical boards impose differing telemedicine laws and restrictions on doctors. Procedures for telemedical treatment are not standardized across State lines.
Looking to the future, telemedicine has the potential to transform the way doctors deliver care, promising improved treatment, and saving more than time and money
source:voipreport.com